Blog
Sampada Prashant Pudke is awarded the Bo Rydin Foundation for Scientific Research Awards for Commendable Master’s Thesis!
The foundation promotes research at Swedish universities and institutes in technical or natural sciences within Essity’s and SCA’s business areas. Essity is a leading global hygiene and health company, and SCA is Europe’s largest private forest owner creating value within forest, wood products, pulp, paper, packaging material, and renewable energy. The aim of the Foundation is to promote scientific research within areas that are of importance for Essity and SCA, respectively. Sampada received...
Digital Cellulose: Pioneering the Future of Sustainable Electronics
In the quest for sustainable and eco-friendly materials, cellulose has emerged as a promising candidate. The article “Digital Cellulose: Recent Advances in Electroactive Paper” delves into the innovative world of electroactive paper and its potential applications in sustainable electronics. What is Electroactive Paper? Electroactive paper is a type of smart material made from cellulose and an electroactive material. This material combines the natural abundance and biodegradability of cellulose...
Digital Cellulose Center Masters Student Highlight – Sampada
In the latest feature from the Digital Cellulose Center, we spotlight Sampada Pudke, a dedicated master’s student making waves in the field of sustainable materials. In her insightful video, Sampada delves into her groundbreaking work on creating graphene from materials often considered waste in the forest industry. Transforming Waste into Wonder Sampada’s research focuses on the innovative use of a laser to turn forest industry by-products into graphene, a material renowned for its...
DCC Partner Highlight! Cellfion: Pioneering Sustainable Membrane Technology
In an era where sustainability is more crucial than ever, Cellfion stands out as a beacon of innovation and environmental responsibility. This Swedish company is revolutionizing the field of membrane technology with its cellulose-based solutions, derived from wood. A Green Alternative to PFAS Cellfion’s membranes offer a sustainable alternative to traditional PFAS-based membranes. By utilizing cellulose, an abundant and renewable resource, they are paving the way for greener technologies in...
The future is transdiciplinary! This year’s TechMark Arena is concluded.
TechMark Arena is a transdisciplinary academy at RISE Research Institutes of Sweden that brings together master’s students and supervisors from various backgrounds in order to work on a common theme. The financiers for this year’s initiative were RISE, Gunnar Sundblads forskningsfond, Sio Grafen and the Digital Cellulose Center (DCC). The idea for TechMark Arena came from a desire for better cooperation around biobased materials. The name TechMark comes from the words Technology and Market,...
Towards Green Electronics in Europe
Watch the Digital Cellulose Center’s webinar on Green Electronics in Europe with Dagmawi Belaineh from RISE. Dagmawi presents the main takeaways from the White Paper “ECS Sustainability and Environmental Footprint,” authored by the European Association on Smart System Integration (EPoSS). The White Paper addresses the sustainability and environmental impact of electronic components and systems (ECS) within Europe and provides an overview of the current state-of-the-art in green ECS and the...
How will the PFAS directive impact electronics
There is a strive to phase out PFAS chemicals since they are highly persistent and accumulate in nature. How will the PFAS directive affect the electronics industry? RISE Research Institutes of Sweden's PFAS expert, Lisa Skedung, joined the Digital Cellulose Center Seminars to give a talk about PFAS and the broad restriction proposal that is now being evaluated by ECHA committees and how it may affect the electronics industry. Watch Lisa Skedung's talk, where she introduces PFAS chemicals and...
Digital Cellulose Center’s webinar series
Join the Digital Cellulose Center's webinar series this autumn on topics such as green electronics, PEFAS in electronics, and 3-D printing for electronics. The vision of the Digital Cellulose Center (DCC) is to make lignocellulose-based products an integral part of a sustainable, digital society. The research and development is targeting biobased and green electronics. The DCC seminars are lifting challenges and opportunities faced by the electronics, energy storage, and biorefinery...
New partners: Norrköping Science Park and ParsNord
Norrköping Science Park and ParsNord join the Digital Cellulose Center as new partners, contributing to shaping an innovation cluster within digital cellulose and creating new sustainable energy storage solutions. "We are very excited for Norrköping Science Park (NOSP) and ParsNord to join the Digital Cellulose Center as partners," says Ursula Hass, Centre Director at Digital Cellulose Center. "NOSP's participation represents a new step towards developing a research-based innovation cluster...
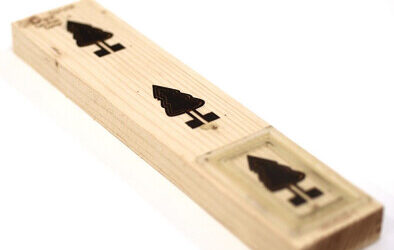
Bio-based moisture sensors for wood
Researchers from the Digital Cellulose Center have developed a bio-based sensor that can detect both humidity and moisture inside the wood, as well as in the surrounding area. Using these sensors can lead to more sustainable buildings as well as help prevent moisture damage and hazardous mold. "These sensors can lead to more sustainable wooden buildings and other constructions without relying on critical materials. At the same time, they become easy to handle at end of life, since they do not...